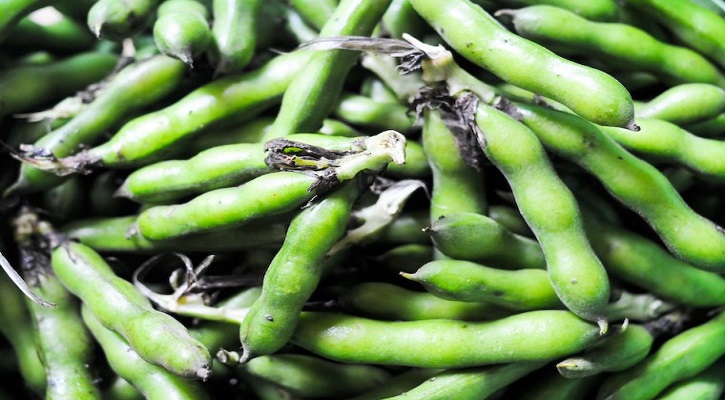
Fava Beans
- Womenscorner Desk
- September 20, 2020
Vicia faba, also known in the culinary sense as the broad bean, fava bean, or faba bean, is a species of flowering plant in the pea and bean family Fabaceae. It is of uncertain origin:160 and widely cultivated as a crop for human consumption. It is also used as a cover crop. Varieties with smaller, harder seeds that are fed to horses or other animals are called field bean, tic bean or tick bean. Horse bean, Vicia faba var. equina Pers., is a variety recognized as an accepted name.
Read More : Low Carb Diets Help You Burn Fat
Some people suffer from favism, a hemolytic response to the consumption of broad beans, a condition linked to a metabolism disorder known as G6PDD. Otherwise the beans, with the outer seed coat removed, can be eaten raw or cooked. In young plants, the outer seed coat can be eaten, and in very young plants, the seed pod can be
eaten.
Nutrition : Fava beans are 11% water, 58% carbohydrates, 26% protein, and 2% fat. A 100 gram reference amount supplies 341 calories and numerous essential nutrients in high content (20% or more of the Daily Value, DV). Folate (106% DV) and dietary minerals, such as manganese, phosphorus, magnesium, and iron (range of DV 52 to 77%). B vitamins have moderate to rich content.
Read More : To Loss Fat Eat Fewer Carbohydrates
Health concerns :
Toxicity : Beans generally contain phytohaemagglutinin, a substance that occurs naturally in plants, animals and humans. The relatively low toxin concentrations found
in V. faba can be largely destroyed by boiling the beans for 10 minutes.
Genetic predispositon : Sufferers of favism must avoid broad beans, as they contain the alkaloid glycoside vicine and may initiate a hemolytic crisis. Broad beans are rich in tyramine, and thus should be avoided by those taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors.
Source : Google