Drug Abuse and Depression
- Womenscorner Desk
- November 25, 2020
Depression may be a common condition that's related to an increased risk for other chronic health problems, including drug abuse. When an individual is depressed, it are often tempting to alleviate depressive symptoms by turning to drugs and/or alcohol. An estimated one-third of individuals with clinical depression engage in drug abuse as a sort of self-medication to alleviate feelings of hopelessness, low-self-opinion, and despair.
Although these chemical intoxicants may temporarily relieve symptoms, they will also make depression more severe and trigger or intensify the negative feelings and self-destructive behaviors related to depression. People who have depression are at an approximately 10% lifetime risk of suicide, a risk that increases to 25% if drug abuse is added to the equation. The substances also can become addictive, with the body becoming more hooked in to their effects, the more an individual uses them. during this way, depression and substance abuse feed into one another , with one condition often making the opposite condition worse.
Read More : Some Vegetables & Fruits that can Replace Bread!
Over time, drug abuse might not only intensify depressive symptoms but also eventually cause health problems like brain damage.
Dual diagnosis : According to the US National Institute on substance abuse , data indicate that folks who are diagnosed with a mood disorder are at double the danger of developing a substance use disorder, compared with people that don't have a mood disorder.
A national survey by The drug abuse and psychological state Services Administration found that in 2014, approximately 7.9 million adults within the us had two co-existing psychological state problems like depression and drug abuse. Data gathered by the University of Utah also showed that 27% of individuals with major depressive disorder have a white plague. When disorders co-occur during this way, the term “dual diagnosis” is employed.
Risk factors for depression and drug abuse : Certain people are at an increased risk for depression and therefore an increased risk for a substance use disorder. These include:
- Middle-aged individuals between 45 and 64 years old
- African Americans
- Hispanics
- People who have been unemployed for a long time
- People who are unable to work
- People who do not have medical insurance
Read More : How Much Fat Should You Eat in a Day?
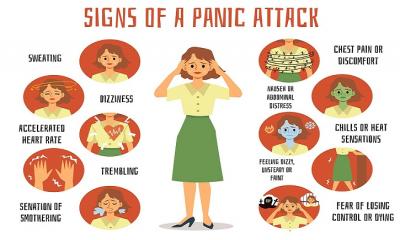
People suffering from depression experience more than occasional feelings of sadness and symptoms can manifest physically, as well as mentally. Some common symptoms of depression include:
- Loss of interest in hobbies, socializing activities, work, and personal goals
- Feelings of pessimism, worthlessness, and hopelessness.
- Irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Difficulty sleeping or sleeping too much
- Appetite and weight changes
Most people experience at least one of these common symptoms at some point in their life, but for people with clinical depression, multiple symptoms persist for at least 2 weeks can become extremely dangerous. Signs of severe depression include suicidal thoughts, self-destructive behaviors and hallucinations or delusions.
Read More : Chilli Pepper Help You To Live a Long and Healthy Life
Shared factors contribute to depression and substance abuse : Research has shown that a lot of of the factors involved in depression also contribute to substance use disorders. for instance , both conditions seem to stem from problems involving an equivalent brain chemicals and pathways, also as factors like case history and former trauma. Studies have shown that folks with depression have lower levels of dopamine; drugs of abuse also are known to change dopamine levels. The hormone serotonin is that the neurotransmitter most ordinarily related to depression and other mood disorders. Similarly, people with alcoholism have alterations to serotonin receptors.
Among people with certain mental health disorders, reward pathways in the brain are dysfunctional. Similarly, people who abuse cocaine also seem to have dysfunction in these reward pathways.
Stress and trauma during childhood : Stress and trauma during childhood also increase a person’s risk of developing both depression and a substance abuse disorder later in life. Examples of events that may trigger childhood trauma and stress include the death of a parent, sexual or psychological abuse, domestic violence, and neglect.
Read More : Can Rice Help You Lose Weight?
The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation states that, while an association between childhood trauma and depression in adulthood does exist, further research is required to determine why susceptibility to depression is more common in these individuals. Clinical research has suggested that exposure to worry during childhood lowers levels of the “feel-good hormone” oxytocin, which affects feelings of trust and bonding. A brain region called the hippocampus, which is involved in memory and emotion, also tends to be smaller in people that suffer from chronic stress.
According to the National Child Traumatic Stress Network, some research has shown that children who are exposed to trauma, experience stress regularly, or have post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) are at an increased risk for drug abuse . The studies indicated that between one-quarter and three-quarters of individuals exposed to childhood trauma started using substances of abuse to assist them deal with their feelings. Studies have even shown that these people find it difficult to prevent using the substances because the negative emotions then start again.
Treatment of a dual diagnosis : Treatment for a dual diagnosis of depression and substance abuse usually attempts to treat both conditions simultaneously. Without proper treatment for the depression that drives addiction, or vice versa, patients are at risk of returning to their addictive behaviors or experiencing a recurrence of depressive symptoms.
Read More : Some Best Aerobic Exercises for Weight Loss
Treatment usually involves a combination of medication and therapy. Antidepressants may be prescribed to help stabilize mood and drugs that help patients withdraw from substances may be used, as required. At the backbone of treatment are therapies such as individual counseling and group therapy to provide a stable foundation for addressing the problems that are related to both disorders.